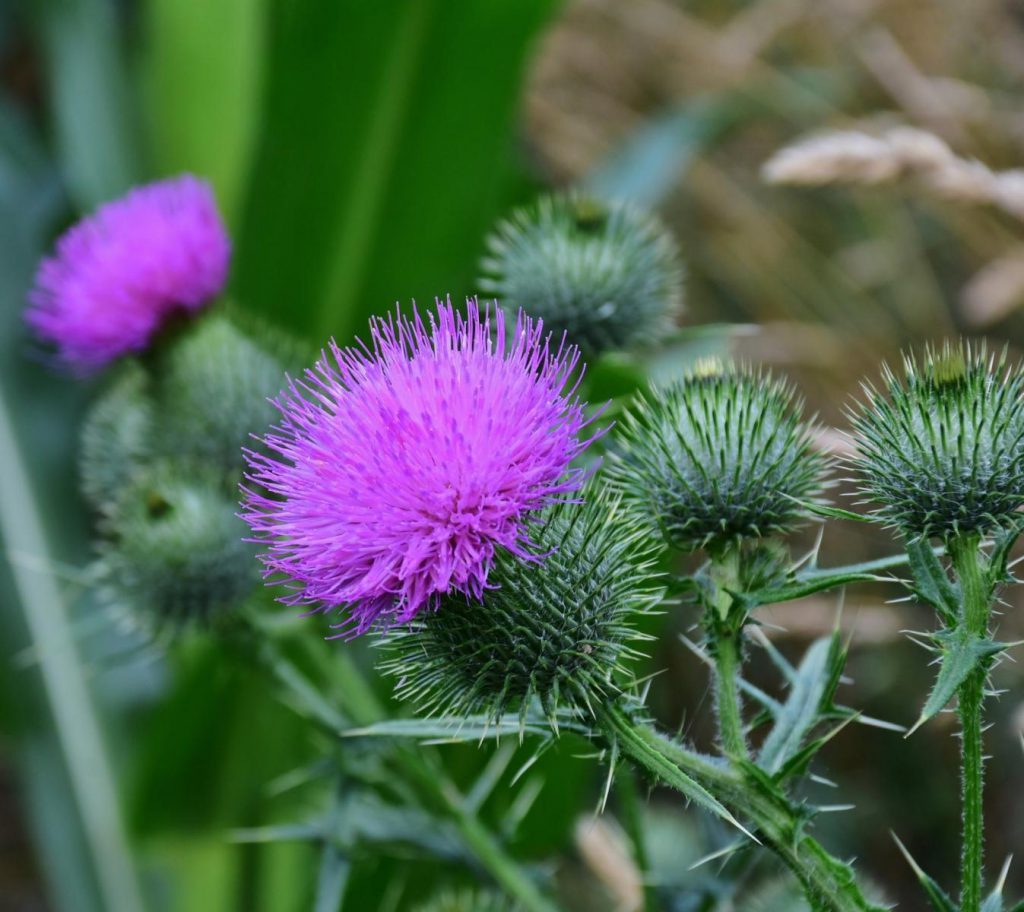
What is silymarin and in which plant?
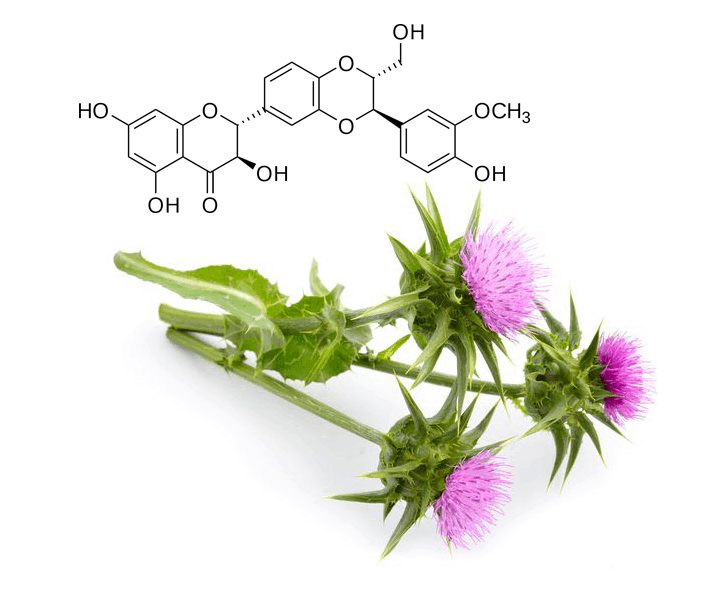
Milk thistle has the scientific name Silybum marianum, this is a tree with long, thin stems, thorny leaves and purple-red flowers at the top. The group of active ingredients found in milk thistle known collectively as silymarin has antioxidant, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties. Milk thistle is used medicinally to treat diseases of the liver and gallbladder.

Uses of Silymarin
- Silymarin is an antioxidant that can neutralize damaging free radicals:
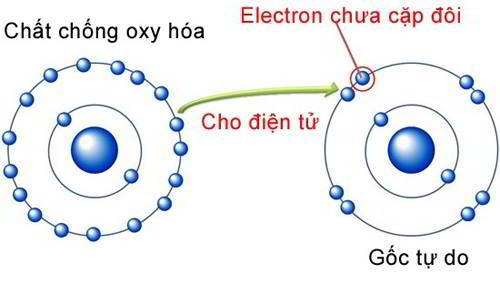
As a flavonoid, Silymarin can neutralize free radicals (such as lipoperoxid) that are produced when the liver is inflamed or damaged.
- Silymarin helps stabilize liver cell membranes and prevent toxins from infecting liver cells:
This is the liver detoxification mechanism of Silymarin. In many studies using mouse models, Silymarin has been shown to protect liver tissue from toxicity caused by hepatotoxic substances such as paracetamol, alcohol, CCl4 …
- Silymarin enhances the synthesis of ribosomal RNA (ribosomal RNA synthesis), helps protein synthesis to promote the repair of damaged liver cells and stimulates the growth of new liver cells.
In a study based on galactosamine-induced liver inflammation, peritoneal injection of silymarin at a dose of 140 mg/kg/day for 4 days inhibited the harmful effects of galactosamine for better protein production in the rat liver.
- Silymarin inhibits the transformation of the liver into fibrous tissue, reduces the formation of collagen fibers leading to cirrhosis.
In one study, silymarin was shown to reduce the formation of isolated stellate cells from rat liver by 75%, thereby reducing the transformation of astrocytes into collagen fibers leading to cirrhosis.
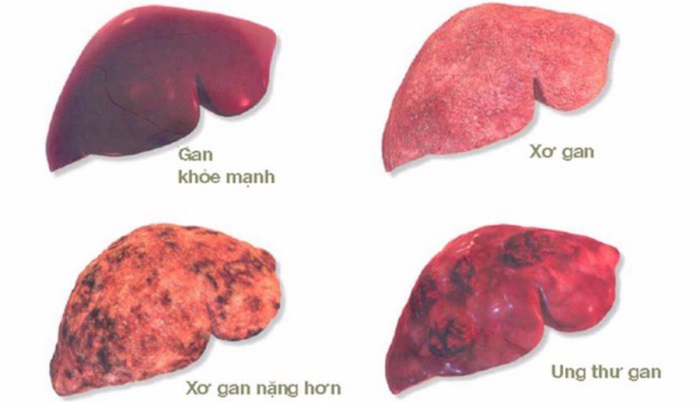
Thus, Silymarin is an active antioxidant, antiviral and anti-inflammatory. This is really a savior for people with liver diseases, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis or liver damage.