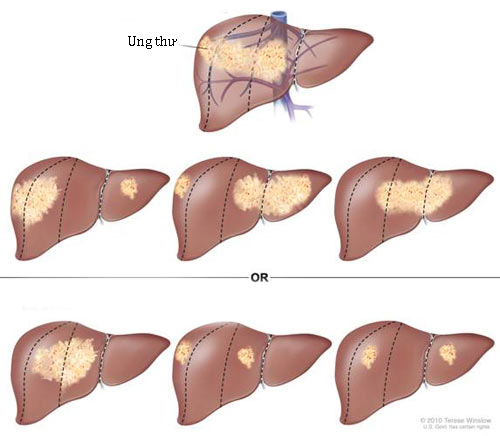
Primary liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer globally and the second leading cause of cancer death. More than 95% of people are diagnosed with liver cancer by age 45 or older. Liver cancer is difficult to recognize early due to poor symptoms and easily ignored by patients. Once detected, it is advanced, difficult to treat and has a high mortality rate. However, liver cancer is considered the easiest to prevent by reducing exposure to known risk factors for the disease.
With cancer still confined to the liver, the 5-year survival rate is 28%. When cancer has grown into nearby organs or has spread to nearby lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is only 7%. Cancer has spread to distant organs, only 2% of patients live to 5 years.
– Chronic viral hepatitis: The most common risk factor for liver cancer is chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus HBV or the hepatitis C virus. These infections lead to cirrhosis, which progresses to cancer. liver.
Causes of liver cancer
– Heavy alcohol use, alcoholism is the cause of cirrhosis.
– Obesity can lead to fatty liver disease and cirrhosis, increasing the risk of developing liver cancer.
– Diabetes is associated with an increased risk of liver cancer. People with type 2 diabetes tend to be overweight or obese, which can cause liver problems.
– Aflatoxins poisoning by eating molds in moist grains such as beans, corn, etc. Carcinogens produced by a fungus that can contaminate peanuts, wheat, soybeans, corn and rice. Long-term exposure to these substances is a major risk factor for liver cancer. The risk is increased even more in people with hepatitis B or C infections.
1. Signs of liver cancer
Most have no signs and symptoms in the early stages. When symptoms do appear, they can include unexplained weight loss, loss of appetite, upper abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, enlarged liver, swollen abdomen, jaundice, and yellow eyes.
2. Prevention of liver cancer
– Avoiding important risk factors for liver cancer is chronic infection with the HBV and HCV viruses. These viruses can be spread from one person to another through unprotected sex, from a mother to her baby during childbirth. It can be prevented by not sharing needles and by practicing safe sex like using condoms.
– Prevent HBV by getting vaccinated. There is no vaccine for HCV. Treatment of chronic hepatitis caused by viruses B and C if infected with these 2 viruses. Treatment reduces the amount of virus in the blood and reduces liver damage, which in turn reduces the risk of liver cancer.
– Limit alcohol use. Not drinking alcohol or drinking only in moderation can help prevent liver cancer.
– Avoid obesity.
– Limit exposure to cancer-causing chemicals.
3. Early detection of liver cancer.
For people at high risk for liver cancer, which is cirrhosis (from any cause) or chronic hepatitis B, C infection… should be screened for liver cancer by testing blood for alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and ultrasound every 6-12 months.
AFP is a protein that may be present at elevated levels in patients with liver cancer. But looking at AFP levels is not a perfect test for liver cancer. Many patients with early liver cancer have normal AFP levels. In addition, AFP levels can be increased from other cancers that are not liver cancer.