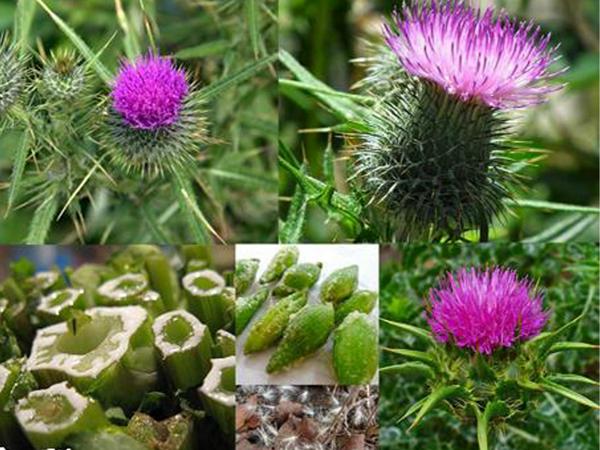
Milk Thistle
English name: Milk Thistle, St. Mary’s Thistle.
Vietnamese name: Milk thistle, milkweed, chrysanthemum.
Scientific name: Silybum Marianum.
Origin: Mediterranean region.

- Description
The growth environment of milk thistle is dry, sunny areas. Mature milk thistle from 1.2m to 3m tall; large leaves with white spots or veins; purple-red cotton; The fruit is small, with a hard, glossy brown skin with many dots. The whole stem and leaves have tiny thorns that pierce the skin very painfully, so people have to wear thick gloves when harvesting.
- Pharmaceuticals and uses
2.1. Drugs
Over the past 50 years, scientists have been successful in identifying the active ingredients in milk thistle, most notably a group of three related substances known collectively as silymarin. This substance consists of a mixed group called flavonolignands (silybinin, silychristin and silydianin) that are commonly known as silymarin. Most milk thistle products are properly formulated and its essence extracted from the seeds and fruit contains between 70 and 80 percent flavonolignands.
2.2. Uses
Experiments have definitely demonstrated that silymarin protects the liver from a variety of toxic agents. Milk thistle has been used in Europe as a liver remedy for thousands of years. During the first century AD, milk thistle was noted for its excellent hepatoprotective properties, while assisting the liver in maintaining normal function and was extremely effective in helping to treat a variety of ailments. liver, including cirrhosis, viral hepatitis and liver damage caused by drug and alcohol abuse.
2.2.1. Proven Uses:
Stabilizes the membranes of liver cells, preventing the penetration of toxic substances into the liver.
Enhances the synthesis of ribosomal RNA (ribosomal RNA synthesis), helps protein synthesis to promote the repair of damaged liver cells and stimulates the growth of new liver cells.
Inhibits the transformation of the liver into fibrous tissues, reduces the formation and deposition of collagen fibers leading to cirrhosis.
Anti-lipid peroxidation (antioxidant), increase the liver’s ability to oxidize fatty acids, stabilize inflammatory cells, inhibit inflammatory response, reduce liver enzyme levels, improve symptoms symptoms of liver disease such as fatty liver, hepatitis.
Increases intracellular levels of intracellular glutathione, which is essential for the detoxification response of hepatocytes.
2.2.2. The uses are still under research:
Preventing the oxidation of LDL cholesterol into plaques that stick to the artery walls, which is the cause of atherosclerosis.
Strengthens intestinal motility and prevents toxicity, cleans the kidneys and aids excretion. Especially milk thistle can dissolve kidney stones and gallstones.
Relieves menstrual pain and is a valuable premenstrual support herb.

- Contraindications
Use of milk thistle may also occur, but very rare, side effects, including: vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, headache, heat rash, joint pain, impotence (physiological) ), short and rapid breathing, unconsciousness,…
Silymarin extract from milk thistle may interact with some other medications such as schizophrenia; medicine to treat cerebrovascular accident; anesthesia.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not use milk thistle
For more information:
The effects of silymarin extract from milk thistle (milk thistle, chrysanthemum) have been tested on humans or animals. Some of the uses have been widely publicized; others are under research.
References:
1/ Milk Thistle – A Remarkable Flavonoid Antioxidant And Liver Protectant.
Milk thistle (milk thistle, chrysanthemum) contains the medicinal substance silymarin extracted from the seeds of the plant, which has antioxidant effects and protects the liver against toxins from alcohol, drugs and other substances. other hepatitis agents.
2/ Monograph: Silybum Marianum (Milk Thistle).
Milk thistle (milk thistle, chrysanthemum) contains silymarin, which helps protect the liver effectively. The effects of silymarin: anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, increase protein synthesis of liver cells, thus promoting liver tissue recovery. The adult dosage is between 100-300mg of standardized silymarin extract in capsule form in 3 divided doses daily.
3/ Possible Combinational Effect of Silymarin with Hepatoprotective Plants in Ameliration of Hepatic Insufficiencies.
The use of silymarin, which is extracted from the seeds of milk thistle (milk thistle, chrysanthemum) every day at a low dose combined with a few herbs with liver tonic effects will help protect the liver, improve liver function, and improve liver function. significantly improve liver function.
4/ Silymarin as a potential hypocholesterolaemic drug.
The pharmaceutical substance silymarin is extracted from milk thistle (milk thistle, chrysanthemum). Studies show the potential of this drug to limit cholesterol synthesis in the liver, thereby helping to protect heart health.
5/ Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) – Evidence.
The medical website presents evidence for the uses of milk thistle (milk thistle, chrysanthemum), some of which have been shown to treat cirrhosis, chronic liver disease; there are others that need further research such as treatment of acute viral liver disease, Amanita phalloides mushroom detoxification, liver cancer, diabetes (in patients with cirrhosis), digestive disorders, high cholesterol, damage Drug and toxin-induced liver, menopausal symptoms.
6/ American Cancer Society – Milk Thistle.
According to the American Cancer Society: silymarin extract from milk thistle (milk thistle, chrysanthemum thorn) is a combination of 3 drugs – silybinin, silydianin and silychristin – with antioxidant effects. Other uses of milk thistle: help treat liver diseases (cirrhosis, viral hepatitis and liver damage caused by drug and alcohol abuse). Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not use milk thistle.
7/ Possible Interactions with Milk Thistle.
Milk thistle (milk thistle, chrysanthemum) contains the medicinal substance silymarin, which has the function of protecting the liver against toxins from the external environment entering the body, however, silymarin extract also interacts with a number of other substances. certain medications such as those for schizophrenia (schizophrenia); drugs to treat cerebrovascular accident; anesthetics or numbing drugs (anesthesia).
Currently, OIC NEW is researching to launch products specialized in supporting the treatment of liver diseases, OIC NEW will offer a product that brings good effects to consumers’ health, and is completely extracted from natural herbs. Applying nanotechnology to achieve the highest efficiency for each product.